OAuth 2.0 Server Flow
The OAuth 2.0 server authentication flow is used whenever a Constant Contact account uses your integration for the first time. The Constant Contact user must login to their account and give permission to your application to access their Constant Contact account. The Server Authentication flow consists of 2 main transactions:
- The app makes an authorization request
- The authorization server responds with an authorization code.
- The app then makes an access token request using the authorization code.
- The authorization server responds with an access token.
The interactions between the user, the application, and the Constant Contact Authorization Server are illustrated here.

- The Constant Contact user opens your application for the first time.
- The application directs the user to the Constant Contact authorization server (see Authorization Request for details).
- The user authenticates with Constant Contact and grants the application access to their account.
- The authorization server redirects the user to the application using the redirect URI, and provides an authorization code if the user granted access to the application (see Authorization Response for details).
- The application then exchanges the authorization code for an access token for use in all API calls for that account (see Access Token Request for details)
For users without a Constant Contact account
You have two options to allow users to sign up for a Contact Contact account if they don't already have one when they launch your app. The first option adds a sign up link to the login page by using the oauthSignup query parameter. The second option allows you to ask users if they have an account when opening your app for the first time. If they answer no, use the newUser query parameter to direct them to the account sign up page.
Option 1: Using the oauthSignup Query Parameter
Use oauthSignup=true in the Authorization request to display "Dont have an account? Sign up free" in the top right of the login screen. This gives users who don't have an account the ability to sign up for an account and grant access to the new account.
 |
 |
|
Login window when oauthSignup=false
(see parameters table below for more info)
|
Login window when oauthSignup=true |
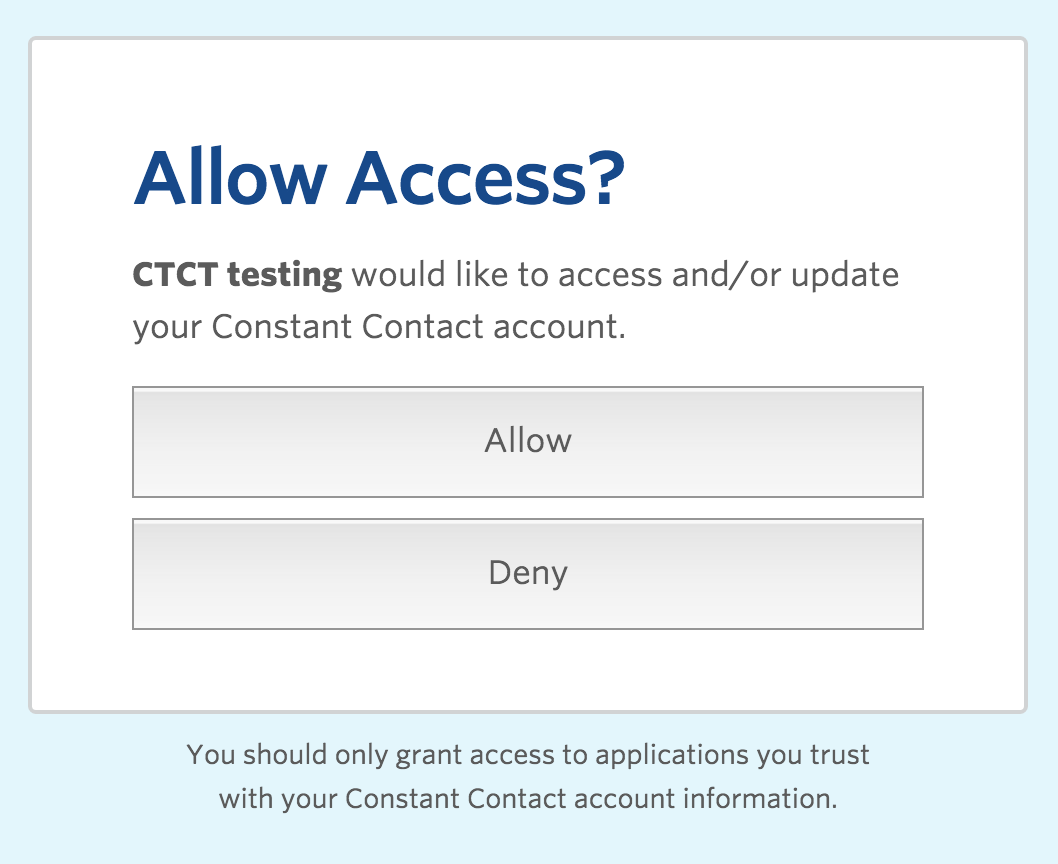
Allow Access prompt:
Option 2: Using the newUser Query Parameter
When set to true, the newUser query parameter sends the user to the account signup form to create a new trial account, and then on to the Allow Access screen. This gives you the option to ask the user if they already have a Constant Contact account when they initially launch your app. If they do, you use the traditional grant access flow where the user logs in to their account, and then Allows Access.
If the user does not have an account, use newUser=true in the Authorization Request to send the user to the Account Signup page. After signing up for a free trial account, the Allow Access screen displays.
 |
 |
|
|
Create Account page shows when using
newUser=true (see parameters table below for more info)
|
Allow Access displays after user creates new account. |
Authorization Request
An Authorization Request is formed as a GET call to the authorize API endpoint.
https://oauth2.constantcontact.com/oauth2/oauth/siteowner/authorize |
|||
|
Parameter |
Values |
Req'd |
Description |
response_type |
code |
YES |
A value of code tells the authentication server it is sending an authorization code to a web server. MUST always be code for server applications. |
client_id |
<your_API_KEY> |
YES |
Identifies the app that is making the request to the server; this parameter MUST always be set to the exact value of the API_key. |
redirect_uri |
<your_encoded_redirect_URI> |
YES |
Tells the Authorization Server where to send the user once access is granted. This must be the same redirect_uri that is associated with your API key in Mashery. |
pn |
<your_encoded_partner_name> |
NO |
Use this to attribute new accounts created using the sign up link on the Oauth flow page to a partner. Do not include this parameter if you're not a Constant Contact partner. |
oauthSignup
|
true or false(default) |
No |
Use NOTE: This parameter is ignored when using |
newUser
|
true or false(default) |
No |
Use |
Example: Authorization Request for the server flow:
GET https://oauth2.constantcontact.com/oauth2/oauth/siteowner/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=187775cfde5143b&
redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.myapplicationurl.com
You can include additional query parameters with an Authorization request by appending them to the redirect URI and encoding it, as follows:
GET https://oauth2.constantcontact.com/oauth2/oauth/siteowner/authorize?
response_type=code&client_id=187775cfde5143ba92187c985fa63dd6&
redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.myapplicationurl.com%3FqueryParam1%3DqueryValue1
%26param2%3Dvalue2%26param3%3Dvalue3
Authorization Response
If the user grants the access request, the authorization server issues an authorization code and delivers it by adding it to the query component of the redirect URI.
|
Field |
Description |
code |
Unique 27 character authorization code generated for the request. It is valid for 10 minutes, and must be exchanged for an access token in order to make API calls. |
error |
Error label and description if an error condition is detected in the authentication request. |
Example: Authorization Response for the server flow
<your_encoded_redirect_URI>?code=fuOJtFn7K6srQ37wC576A6azI5h&username=<constant_contact_username>
NOTE: If a user's account has been inactive (user never logged in) for the 3.5 years prior to April 1, 2013, it has been deactivated. These accounts cannot be reactivated and are not able to obtain an access token. The Authorization Response for these accounts is:
<your_encoded_redirect_URI>?error=access_denied&error_description=This+account+is+no+longer+valid
These are some of the response codes that the system provides during the authentication flow.
| Code | Message | Description | |
|
N/A |
access_denied | The resource owner or authorization server denied the request. | |
|
400 |
invalid_request |
The request is missing a required parameter, includes an unsupported parameter or parameter value, or is otherwise malformed. |
|
|
401 |
unauthorized_client |
The client is not authorized to request an authorization code using this method. |
|
|
401 |
The client_id <client_id> is not valid or has been disabled |
The client_id provided in the request is not valid. Message is returned after the Constant Contact customer provides their credentials. |
|
|
401 |
A client_id parameter must be supplied |
The client_id parameter is missing from the Authorization Request. |
|
|
400 |
A valid response_type must be supplied |
Either the response_type is missing, or the value is invalid; value must be "code" for server flow. |
|
|
400 |
A redirect_uri parameter must be supplied |
Authorization request did not include a redirect_uri parameter. |
|
|
403 |
Invalid redirect |
The redirect_uri provided is not valid or is different from Mashery application settings. |
After the application receives the authorization code, it must exchange it for an access token by making a call to the Token endpoint.
- The application requests an access token from the Constant Contact authentication server, providing its
client_id,client_secret,redirect_URIand theauthorization_code. - The authorization server validates the client credentials, the authorization code, and the redirect_URI (ut must match the redirect_uri used in the Authorization Request exactly, including any parameters added). If the validation is successful, the authorization server sends back an access token. The application needs to retain the access token and use it when making API calls on behalf of the user.
The request is formed as a POST to the Token endpoint, defined as follows:
https://oauth2.constantcontact.com/oauth2/oauth/token? |
|||
|
Parameter |
Values |
Req'd |
Description |
| grant_type | authorization_code |
YES |
This parameter MUST always be set to 'authorization_code' |
| client_id | <your_API_KEY> |
YES |
This parameter MUST always be set to the value of <your_API_KEY> |
| client_secret | <your_client_secret> |
YES |
This parameter MUST always be set to the <your_client_secret> value associated with the API_key. |
| code | <unique_code> |
YES |
MUST be set to the authorization code provided in the Authorization request response. |
| redirect_uri | <your_encoded_redirect_URI> |
YES |
It must match the redirect URI used in the authorization request, including any parameters. |
Example: Access Token Request for the server flow
POST https://oauth2.constantcontact.com/oauth2/oauth/token?grant_type=authorization_code&client_id=<your_API_KEY>&client_secret=<your_client_secret>
&code=<unique_code>&redirect_uri=<your_redirect_URI>
Access Token Response
A successful response to this request contains the following fields:
|
Field |
Description |
|
access_token |
hyphenated hexadecimal string used to make API calls to a users account |
|
expires_in |
315359999 seconds - Tokens are currently valid for 10 years |
|
token_type |
This is always set to Bearer |
A successful response is returned as a JSON array:
{
"access_token":"a46950a6-7cad-413a-8183-550756d096f4",
"expires_in":315359999,
"token_type":"Bearer"
}
OAuth 2.0 Server Flow PHP Example
Check out sample PHP code that implements the OAuth 2.0 server flow in this Github repository.
